| Multi_R_Designer Tutorial |
1) Start a new project by
selecting Start new query ![]() .
.
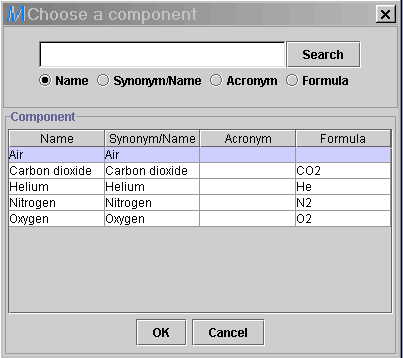
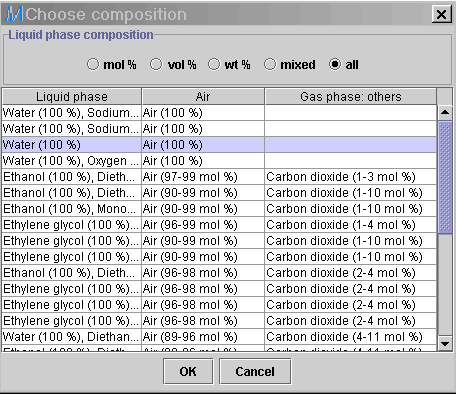
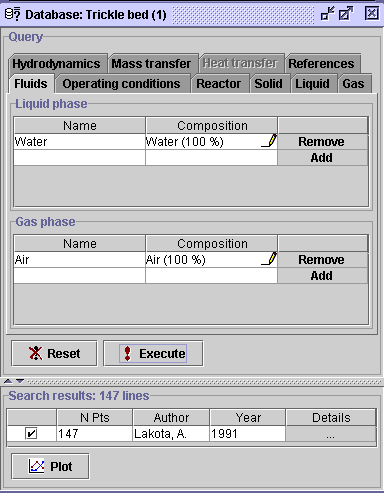
2) Apply the following problem specifications, namely the Liquid composition: Water (100%) and Gas composition: Air (100%).
 |
 |
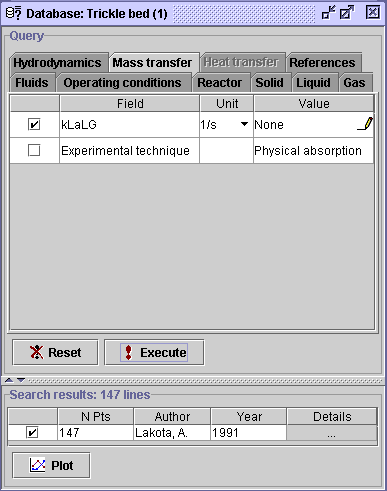
Comment: Oxygen diffusion
in water is known to be a physical absorption process. Therefore, it is
not necessary to specify the experimental technique in the Mass transfer
tab. Nevertheless, the list is reduced to a single case, which is Physical
absorption (With a single choice, the combo box ![]() disappears).
disappears).
 |
 |
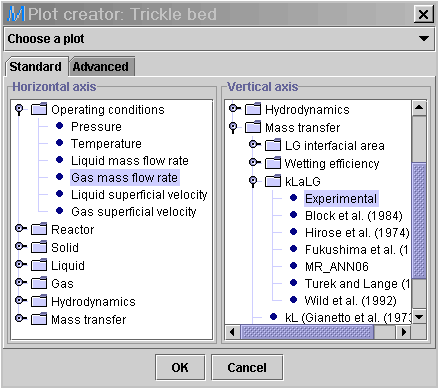
3) Select the Plot
button ![]() ,
then choose Gas mass flow rate (Operating conditions: Gas mass
flow rate) in the Horizontal axis panel and Experimental
(Mass transfer: kLaLG: Experimental) in the
Vertical
axis panel.
,
then choose Gas mass flow rate (Operating conditions: Gas mass
flow rate) in the Horizontal axis panel and Experimental
(Mass transfer: kLaLG: Experimental) in the
Vertical
axis panel.
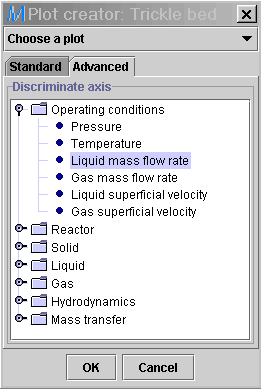
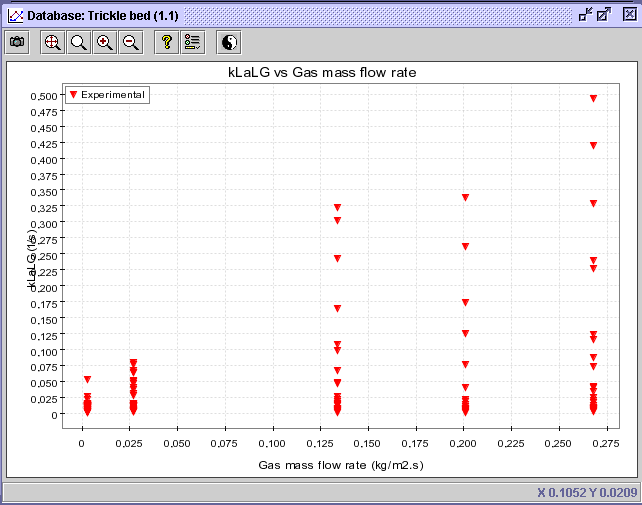
4) In the Advanced
tab, select Liquid mass flow rate (Operating conditions: Liquid
mass flow rate) as the discriminate value. Press OK.
 |
 |
 |
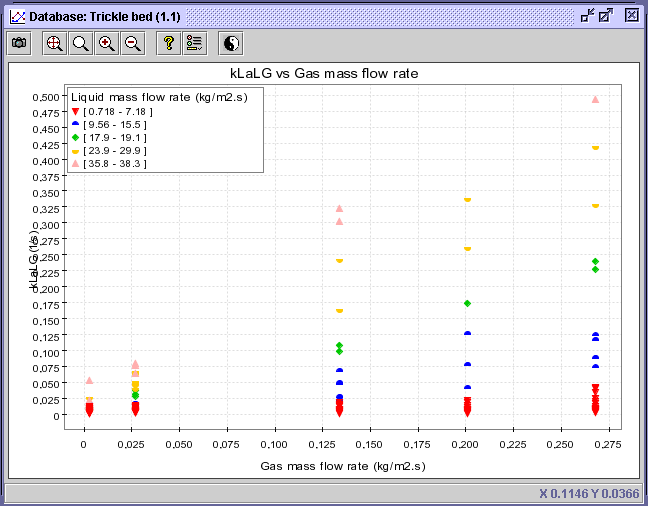
5) Select the Discriminate
series button ![]() and choose the Value discrimination option. Write 5 in the
Number
of classes entry to create 5 equally divided series between liquid
mass flow rates of 0.718 and 38.3 kg/m2s. Press
OK.
and choose the Value discrimination option. Write 5 in the
Number
of classes entry to create 5 equally divided series between liquid
mass flow rates of 0.718 and 38.3 kg/m2s. Press
OK.
 |
6) Save to project ![]() as Case problem 4.2.mr in a folder of your choice.
as Case problem 4.2.mr in a folder of your choice.
CONCLUSION: From the latter diagram, it can be concluded that higher liquid velocity induces larger kLa especially at greater gas mass flow rate.
| Multi_R_Designer Tutorial |