![]() Updated: 12/4/96
Updated: 12/4/96
![]() Updated: 12/4/96
Updated: 12/4/96
All microbes live in an aqueous environment. Without water they either perish or become inactive. The ecology of aquatic environments is complex and our understanding of them are limited. Most aquatic environments teem with life. Microbes have evolved that can live in saturated salt (sodium chloride) solutions at temperatures from below freezing to near boiling; they thrive in waters full of toxic substances like copper, cyanide, lead, silver, gasoline, oil, benzene, and a plethora of other noxious natural and man-made substances. It is a NEAR NATURAL LAW that where water, an energy source and basic nutrients exist, you will find microbes living.
Water is of vital importance to man for several reasons. First, it is required to MAINTAIN LIFE. A person may survive for weeks without food, but only a few days without water. Water is crucial for the growing of our food and the operation of all our industries. Finally, it is a major vehicle of a number of water borne diseases that have shaped history in the past and will certainly continue to do so in the future. For example, the Middle East, where we recently went to war, is mostly a desert with a rapidly growing population of diverse peoples who really don't like one another. The Jordan River, the major source of water for Israel, Jordan and Syria, is, by our standards here in the WATER-RICH Northwest, a trickle that we'd laughingly call a "river". Yet, we are willing to defend one or more of the countries in this region, when their survival depends on this TRICKLE OF WATER that's not much larger than the South Fork of the Palouse that runs through Pullman. Many people consider it likely that the next war in the Middle East may be over WATER and not OIL.
The importance of water in our lives is often overlooked because of its seemingly endless supply. Here in the NW it literally rains down upon us much of the year and if we drive a few miles in any direction we cross humongous rivers spanned by impressive bridges, that they tell us once contained a plethora of fish. Further, a half day's trip takes us to the Pacific Ocean, whose immensity and water content boggles the mind. Finally, 70% of the earth is covered with water, which is a whole lot of WET by anyone's definition. Surrounded by this plentiful supply of moisture it is hard to imagine that we could ever be short of water.
However, as I will demonstrate to you, the addition of a few descriptive terms in front of the word WATER changes the entire picture. These words are: CLEAN, POTABLE, POLLUTED and FRESH. We will be considering water from the microbial perspective of disease. Time unfortunately does not permit the examination of other related areas such as the diversity of microbial forms in aquatic habitats and their influence on the ecosystem.
Because of a need for a stable water supply humans built their communities on or near a water supply. However, this has also led to an unfortunate tendency to dispose of our wastes in the same place where we obtain our drinking water. This presented little problem when the population was small and nomadic, for when the stink of a camp became offensive, we picked up and moved the tribe a few miles up or down stream or over the hill to the next stream. Mother nature then stepped in and rapidly recycled the few wastes left behind. With the coming of AGRICULTURE, PERMANENT SETTLEMENTS and LARGE POPULATIONS, it became impossible to move people to a clean habitat; besides someone usually was already there and they generally took serious umbrage when the new arrivals told them to move on. This probably accounts for the bad attitude of the American Indians towards the settlers. This then sets the scenario: A BURGEONING HUMAN POPULATION UNABLE TO MOVE AWAY FROM ITS WASTE.
![]() FRESH
WATER = non-salt or -sea water.
FRESH
WATER = non-salt or -sea water.
![]() POLLUTION
= Anything that makes water NON-POTABLE.
POLLUTION
= Anything that makes water NON-POTABLE.
![]() SEWAGE
= The combined community waste or all the GARBAGE that we and mother nature
dump into the sewers of a community.
SEWAGE
= The combined community waste or all the GARBAGE that we and mother nature
dump into the sewers of a community.
1. As H increases, Wa tends to DECLINE.
2. As U increases, Wa tends to DECLINE.
3. If U and/or H can be decreased, then Wa INCREASES correspondingly. To put it another way, if you take a 5 min shower as opposed to a 20 minute one, there will be more clean water for everyone.
4. As Wp increases the amount of Wc DECREASES and vice versa. In case you don't understand this let me put it to you in another way. The less POOP we put in the potable water the more POOP-FREE water we have to drink.
5. To increase the amount of Wpw the amount of Wp must decrease.
6. The amount of Wp can only be decreased by NOT ADDING pollution to Wt or by REMOVING pollution from Wp.
It turns out that Wc amounts to less than 1% of the Wt
and (surprise) it is ![]() DECLINING
DECLINING![]() .
.
The first recorded toilets and sewers were built around 3,000 BC in several parts of the world, including the Orkney Islands and India/Pakistan. A system of channels on the Orkney islands drained wastes from toilets in the homes into the sea, whereas cities in India/ Pakistan built open drains 2 ft deep by 7-10 inches wide along major streets through which the wastes were flushed away. Cities in Iran/Iraq had communal toilets in 2,300 BC and the Minoans of Crete had toilets and elaborate sewage systems in their palaces about the same time. Athens in 400 BC piped the wastes from homes to cesspools in the streets.
The Romans, being a social people, favored communal toilets
that could seat 10 to 20 people in public lavatories located over flowing
water to carry the wastes away. It is reported that they carried out business
and politics in these facilities. Perhaps this led to the idea expressed
by many that politics is "in the toilet".
Toilet paper equivalents were a problem and it's likely that most people
used a communal cloth and a pot of water (YUK), reusable sponges attached
to a stick (YUK again), moss, hay/straw (probably where the term "HARD
A.." originated) and/or grass (OUCH). Real toilet paper
appeared in China in 589 AD. It is probably true that EVEN
TODAY most people on the planet do without toilet paper, which
may explain why so many people are in a bad mode much of the time. Larger
Roman cities had extensive sewage systems, some of which still function
today. The larger drains in Rome were big enough the drive a horse and
cart through. In Pompeii one can see the sewage drains running down the
center of the streets. Freiburg Germany (where I spent a sabbatical) has
a system of channels with flowing water running through the town (in which
the community's children now play); these are now "decorative", but in
earlier times they served as the town sewers.


Figure 1. Functional European water systems in Germany and Italy. The picture on the left shows a flowing channel that runs through the city of Freiburg, Germany; it is for show & is not officially used as a sewer. Those channels are hazards for drunk drivers, who frequently end up in them. The picture on the right shows a fountain in an Italian community that still supplies water; note the support bars where buckets are placed when being filled. Behind the fountain is a channel/drain running down the center of the street.
As the population and towns grew in size, the problem
of obtaining fresh, clean water also increased. The Roman world is festooned
with aqueduct ruins, some of which still work, at least over short distances.
A major consideration of every Roman leader was insuring that the citizens
of Rome had a constant clean supply of water. Water was brought to Rome
from the mountains via an extensive system of aqueducts that spanned mountains
and valleys. There were over 250 miles of water conduits inside Rome proper
feeding a system of fountains that supplied citizens with fresh water.
These fountains are still scattered throughout Rome today. Slaves, labored
constantly repairing and maintaining the water system. In India and Pakistan
remains of water pipes of clay sealed with asphalt dating back to 2,700
BC have been found. Copper water pipes were used in Egypt as early as 2,450
BC. For more details on ANCIENT TECHNOLOGY
read "Ancient Inventions" by P. James & N. Thorpe.

![]()
Figure 2. Remains of Roman aqueducts. These are remains of Roman aqueducts. The one on the left, behind that handsome family, is in Yugoslavia, whereas the one on the right is in Italy. At least one Roman aqueduct is still in operation in Spain.
Every water supply system is constantly in danger of contamination. Before the Germ Theory of Disease few people recognized, other than from an aesthetic standpoint, the need for a "clean" water supply. You have seen how, by using statistics, John Snowin 1855, connected polluted water with human disease. We realize today that throughout history most humans routinely drank contaminated water and that this situation still applies to the majority of humans on the planet. When the population was small and scattered, the outbreaks of water borne diseases were confined to concentrations of humans such as those in a single city or army. However, as population increased and travel accelerated, the combination of improved disease transmission, crowding, poverty and ignorance resulted in extensive water borne epidemics and in the water being increasingly contaminated with human fecal waste containing pathogens. Microbes have evolved to take advantage of water as a mode of transmission of intestinal disease. Consider the advantage in transmission for an intestinal pathogen to induce massive diarrhea in a host. (Evolution of Virulence, Sci. Am. Apr. 1993 pg., 86; Discover Mag. Oct. 1995, pg. 111)
Following the collapse of the Roman empire vestiges of
the Roman water technology continued being used throughout Europe. Many
villages and towns piped relatively clean water to central fountains from
near by streams or springs, or diverted streams through channels in the
towns. Centrally placed wells also supplied water in many cities. Sewage
disposal continued to be a severe growth-problem as the size of cities
grew. Many people, lacking toilets, used chamber pots which they emptied
every AM in the streets or alleys. The stench in London in the summers
throughout the middle ages and beyond was reported to cause grown men to
faint and horses to collapse in their harnesses. Slowly however, the idea
of sanitation began to take hold in the 1700s and accelerated through the
1800s. However, Queen Victoria's husband is reported to have died in 1861
of typhoid indicating that even the Royal family apparently drank fecal
polluted water. The idea of supplying water to the inhabitants of cities
developed along with iron technology that made the manufacturing of inexpensive
pipes possible. Private water companies were formed throughout Europe to
supply communities. The idea of filtering polluted water through sand to
purify it appeared first for private homes of the wealthy and later for
municipalities. With the establishment of the relationship between bacterial
pathogens and water polluted with human wastes in the late 1800s, and worldwide
communication that spread the stories of epidemics, people begin demanding
safe water. To meet these demands it, in turn, became necessary to do something
about the prodigious quantities of RAW SEWAGE
spewing forth from cities and industries into the local water sources.
As a consequence, sewage treatment technology developed in the early 1900s,
but it was only applied throughout the US in the last 30 years through
the passage and enforcement of federal laws like the Clean Water Act. As
a microbiologist it is my responsibility to suggest that SERIOUS
CONSIDERATION should be given before removing federal regulations
on water pollution and water standards.

Figure 3. A public fountain still in use in a Swiss mountain town.
![]() TRIVIA QUESTION: Who is considered the inventor of the modern flush
toilet? ANSWER: Thomas Crapper. People said that "he was flush with
success". Consider that if you want your name to roll off the lips
of millions of people everyday what you have to do. Don't find a cure for
cancer or AIDS, or win a war, but invent a better toilet. Then people will
constantly refer to you. Like; "You're full of C......" or "That's a lot
of C......" or,..... well you can think of other examples I'm sure.
TRIVIA QUESTION: Who is considered the inventor of the modern flush
toilet? ANSWER: Thomas Crapper. People said that "he was flush with
success". Consider that if you want your name to roll off the lips
of millions of people everyday what you have to do. Don't find a cure for
cancer or AIDS, or win a war, but invent a better toilet. Then people will
constantly refer to you. Like; "You're full of C......" or "That's a lot
of C......" or,..... well you can think of other examples I'm sure.
The answer is complex. One problem, discussed above, is that people see so much apparently "clean" water around them that it is INCONCEIVABLE that water is in short supply or that it should cost serious MONEY. Another major problem is the PERSPECTIVE that things like water, air and wilderness areas all are part of the COMMONS to be exploited by the many and the RESPONSIBILITY of no one. Finally, there is the problem of the "Frog in the Frying Pan".
![]() Wetlands act as huge sponges ABSORBING
excess water during periods of heavy precipitation.
Wetlands act as huge sponges ABSORBING
excess water during periods of heavy precipitation.
![]() By serving as a place where EXCESS WATER
from rivers and lakes collects and is absorbed, wetlands DECREASE
destructive flooding. Coastal wetlands provide important buffers absorbing
the force of waves from fierce storms thereby minimizing beach erosion.
By serving as a place where EXCESS WATER
from rivers and lakes collects and is absorbed, wetlands DECREASE
destructive flooding. Coastal wetlands provide important buffers absorbing
the force of waves from fierce storms thereby minimizing beach erosion.
![]() The soaking up of the water recharges underground water sources.
The soaking up of the water recharges underground water sources.
![]() Wetlands, especially coastal ones, serve as the habitat for a large number
of species that do not exist elsewhere, such as alligators, numerous fish
species, and large numbers of aquatic birds. Saltwater marshes are the
zones of the HIGHEST BIOLOGICAL
PRODUCTIVITY on earth.
Wetlands, especially coastal ones, serve as the habitat for a large number
of species that do not exist elsewhere, such as alligators, numerous fish
species, and large numbers of aquatic birds. Saltwater marshes are the
zones of the HIGHEST BIOLOGICAL
PRODUCTIVITY on earth.
![]() Water fowl, like ducks, rely upon wetlands for breeding, feeding and over-wintering.
Water fowl, like ducks, rely upon wetlands for breeding, feeding and over-wintering.
![]() Wetlands are the largest. LEAST EXPENSIVE
and MOST EFFICIENT water purification
systems known. The abundant microbial and plant life in wetlands removes
vast quantities of pollutants, producing virtually pollutant-free water.
Wetlands are the largest. LEAST EXPENSIVE
and MOST EFFICIENT water purification
systems known. The abundant microbial and plant life in wetlands removes
vast quantities of pollutants, producing virtually pollutant-free water.
FAQ: "With all these benefits, why are wetlands so controversial?"
ANSWER: "Wetlands are often commercially very valuable.", to whit:
![]() Because wetlands are so FERTILE, FLAT & SHALLOW
they make prime farm land that are inexpensively drained.
Because wetlands are so FERTILE, FLAT & SHALLOW
they make prime farm land that are inexpensively drained.
![]() Because of their vast area, often on the SEA SHORE
or NEAR CITIES, they offer a ready
source of inexpensive, flat land that can be inexpensively filled in (e.g.
San Francisco Bay).
Because of their vast area, often on the SEA SHORE
or NEAR CITIES, they offer a ready
source of inexpensive, flat land that can be inexpensively filled in (e.g.
San Francisco Bay).
![]() Because wetlands are seen as COMMERCIALLY UNPRODUCTIVE
because they don't directly contribute to personal or business taxable
income, they are generally viewed as being "WASTE
LANDS".
Because wetlands are seen as COMMERCIALLY UNPRODUCTIVE
because they don't directly contribute to personal or business taxable
income, they are generally viewed as being "WASTE
LANDS".
![]() Coastal wetland are prime areas for commercial and recreational development;
the lure to turn "seemingly unproductive, mosquito-ridden-swamp
land" into homes, factories, shopping malls and hotels is
powerful as it means jobs, homes and tax money for a region and profits
for the developers.
Coastal wetland are prime areas for commercial and recreational development;
the lure to turn "seemingly unproductive, mosquito-ridden-swamp
land" into homes, factories, shopping malls and hotels is
powerful as it means jobs, homes and tax money for a region and profits
for the developers.
Because current ENVIRONMENTAL LAWS prevent commercial development of many wetlands, even those owned privately, there is IMMENSE PRESSURE to remove these restrictions. Senate bill 1373 (offered Fall of '95), for example, would have allowed the commercial development of huge areas of wetlands across the country, but it did not become law. Currently it is estimated that approximately 50% of the wetland of the US have been lost.
Deciding the balance between keeping and commercializing wetlands is difficult. Destruction of duck habitat, for example, lowers bag limits, shortens the duck hunting seasons and negatively effects the businesses supported by that sport. The increased flooding of lands adjacent to rivers because of the loss of wetlands costs society and individuals money in the form of DAMS & DIKES to control the flooding and DISASTER PAYMENTS for people hurt by the floods, as well as funds to CLEAN UP after floods. All this money comes from the GENERAL TAX FUNDS (that's you and me folks). Polluted water that is purified by passage through wetlands washes directly into rivers, lakes and the ocean once the wetlands are eliminated. The USERS of that polluted water now have to pay for the building of additional WATER-PURIFICATION PLANTS to remove the EXTRA pollutants. The loss of fish from the pollution and destruction of the of the saltwater marsh fish-nurseries is reflected in a DECLINE IN FISH CATCHES with a resultant increase in the PRICE of fish and the LOSS OF FISHING JOBS. It is not easy to determine if the increased taxes and job income that results from the conversion of the wetlands to commercial usage completely covers these losses. It will be most interesting to see the outcome of this struggle.
![]() Did you hear about the witch who parked her broom in a NO
PARKING zone and she was toad!
Did you hear about the witch who parked her broom in a NO
PARKING zone and she was toad!
Raw sewage is rich in organic nutrients such as human excrement, and food and industrial wastes. The purpose of a sewage treatment plant is to provide the optimum conditions for SELECTING & UTILIZING MICROBES to convert EASILY BIODEGRADABLE ORGANIC MATTER (EBOM) to mineral forms like carbon dioxide, nitrate, sulfate, and phosphate. This process is also called MINERALIZATION. Since microbes grow and utilize nutrients most efficiently under AEROBIC CONDITIONS, sewage treatment plants are designed to provide excess OXYGEN for the microbes.
Finally, there is always some material that can not be easily degraded by microbes which SETTLES OUT at various stages in the treatment process. This material is called SLUDGE and it must also be disposed of as part of the sewage treatment process. There are TWO major designs of SECONDARY sewage treatment plants (STP). These are called the ACTIVATED SLUDGE and the TRICKLING FILTER systems. Each of them achieve the SAME EFFICIENCY of treatment, but they use different DESIGNS for doing so.
STEP II: The PRIMARY
SETTLING TANK is a large tank where the flow of sewage slows
down to the point where LARGER PIECES OF ORGANIC
MATTER settles out as SLUDGE.
These tanks also contain a skimmer that picks up smaller floating material,
the majority of which are used condoms. We will deal with the sludge later.
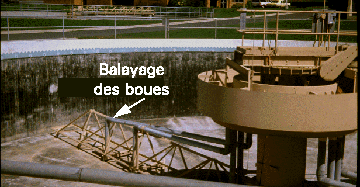
Figure 4. Settling Tank in STP. This is an empty settling tank at the Pullman STP. Note the sweeping arm at the bottom of the tank that slowly rotates and sweeps the settled sludge into the center where it is removed.
STEP III: The third
step in the process involves the AEROBIC metabolism
of the EBOM. In the TF design this
is achieved by spraying the effluent from the primary settling tank over
a 4 to 6 foot pile of large inert blocks of material such as rocks, cement
blocks, redwood blocks etc. (Fig. 5). The spraying saturates the effluent
sewage with oxygen and air circulates between the blocks. The inert blocks
become coated with a layer of microbes that are SELECTED
because they GROW WELL in the sewage
(Fig. 6). This is another example the evolutionary principle of "SURVIVAL
OF THE FITTEST". These microbes absorb the nutrients from the sewage
as it trickles over them and oxidizes (metabolizes) the EBOM to minerals.
Finally the effluent flows into the SECONDARY
SETTLING TANK (Fig. 4). Also 99.9%
of the pathogens are killed during this step.
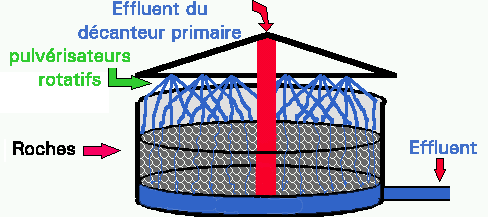
Figure 5. Trickling filter tank design. The effluent from the primary settling tank flows into the spraying arms, which rotate slowly over the rocks or other inert material. As the effluent passes through the air as a fine spray it is saturated with oxygen. The EBOM is removed from the sewage effluent as it trickles over the rocks.
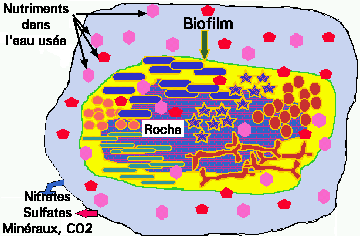
Figure 6. Inert blocks of material covered with sewage digesting microbes. The microbes include bacteria, molds, algae, protozoa, as well as insect larvae. The microbes feed off of the EBOM that flows past them. The oxidized products of microbial metabolism flows out with the effluent into the secondary settling tanks along with chunks of slime that break off from time to time (Fig. 7).
STEP IV: The tank's
design is similar to that of the primary settling tank(Fig4). Large debris,
consisting mostly of chunks of microbial growth that flakes off the inert
blocks, settles out in this tank as sludge. The effluent next flows into
the CHLORINATION BASIN.

Figure 7. Secondary settling tank at the Pullman STP. Its design is essentially the same as the primary settling tank (Fig 4). Note the duck. The young lady who runs the laboratory (Fall 1995), who is a graduate of this department, tells me that they have trouble with the mother ducks bringing their babies to the tank where the babies get trapped in the drain pipes. When this happens she takes off her shoes and wades around the effluent rim to gather up the babies. Now I call that dedication to ducks and faith in the efficacy of the treated sewage.
STEP V: To the effluent
of the secondary settling tank is added sufficient CHLORINE
to kill most the common bacterial pathogens that have survived the previous
treatments. The treated effluent is then released into the environment,
usually a nearby stream, river, lake or the ocean. This treatment however,
does not kill (STERILIZE) all of the
pathogens present so it is unwise to frolic in the water around the sewage
outfall.
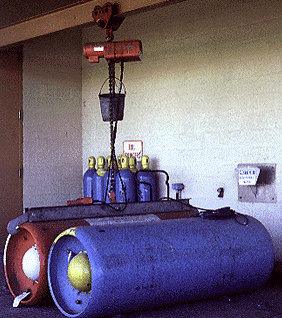
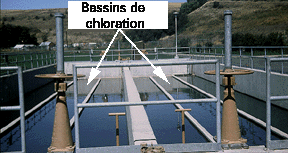
Figure 8. Chlorine treatment of effluent. The photograph on the left shows the large chlorine tanks in the Pullman STP. The chlorine is pumped as a liquid and metered into the effluent from the secondary settling tank. It then flows through the chlorine basins, shown on the right, while the chlorine acts to kill most of the remaining pathogens. The final effluent runs into the environment, in this case the South Fork of the Palouse.
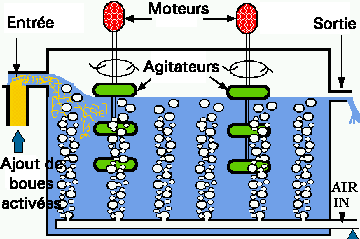
Figure 9. Design of an aeration tank. The air, under pressure is pumped into the tanks and vigorously mixed with the sewage to insure that the material always remains aerobic. Otherwise the stench would cause the neighbors to burn the place down. On the far left, some of the activated sludge that has settled out in the secondary settling tank is mixed with the fresh, incoming, sewage from the primary settling tank. The AS contains hungry microbes that immediately chow-down on all that yummy fresh sewage--makes your mouth water at the thought doesn't it?
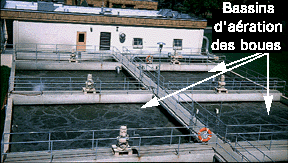
Figure 10. Aeration tanks of the Pullman AS-STP. The Pullman
STP currently has 6 tanks that it operates during the school year. However,
during the summer they shut down half of these for obvious reasons. These
tanks are about 15 feet deep. This flexibility is another advantage to
the AS system. The building in the background houses the large air pumps
and the other pumps for moving the sewage around through the system. Note
in the foreground the "lifesaver". If you fell in would you want to be
saved--maybe if you had kept your mouth shut ![]() .
.
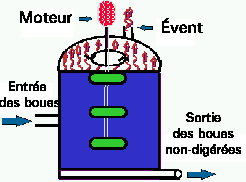

Figure 11. The general design and appearance of an anaerobic sludge digestion tank. The picture on the right shows one of the two Pullman sludge digestion tanks. The sludge from the various parts of the STP are pumped into the thickening tank where it further settles out. The thick concentrate is them pumped into the digestion tanks and fermented for several weeks by anaerobic methane-producing Archaeobacteria during which time 50% of the organic matter in the sludge is converted to methane gas.
At this point 50% of the original sludge's organic material
remains UNDIGESTED and must be DISPOSED
of. Usually this sludge, which comes out a very thick black soup, is pumped
into shallow excavations in the ground and allowed to dry. Alternatively,
if it is safe, it can be pumped onto crop land and used as fertilizer.
The dried material is called DRIED SLUDGE
(talk about a lack of imagination!). In Pullman and Moscow this is not
a lot of this muck, but in places like L.A., Seattle and New York the amount
of daily dried sludge produced is so huge that it threatens to cover the
city or at least a nearby county or two. Disposing of this sludge presents
a really interesting challenge; you might even say large cities are "SLUDGE
CHALLENGED".
It can be burned (contributing to air pollution), buried into TOXIC
LAND FILLS (contributing to ground water pollution) or dumped
into the ocean (contributing to their degradation). If it is safe (no heavy
metals, toxic organic chemicals and the pathogens killed) it makes an excellent
fertilizer for lawns and farms.
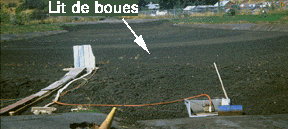
Figure 12. Pullman STP dried sludge bed. It is about 2 acres in size and approximately 6 feet deep. Pullman sludge is of excellent quality and is safe to use as a fertilizer on farms. Several farms in the area request that the undigested be sprayed on their fields.
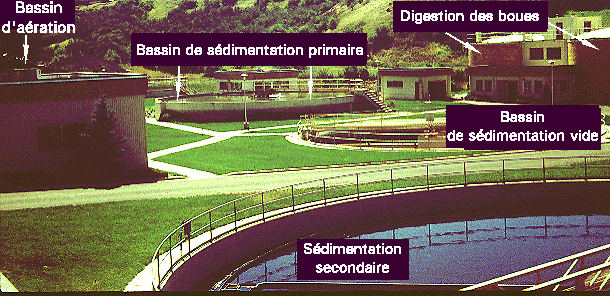
Figure 13. Overview of the Pullman STP from the top of the lab/administration building looking south. The activated sludge aeration tanks are hidden behind the building on the far left which contains the pumps for the plant. Note how green the grass is; why is it so GREEN?
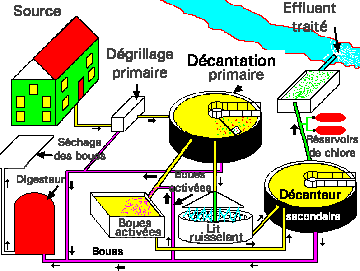
Figure 14. Generalized plan of a secondary sewage treatment plant using either (or both) an ACTIVATED SLUDGE or a TRICKLING FILTER SYSTEM. Note the direction of flow of the various sludges and effluents. If you can draw this plan from memory and describe what each component's purpose is, you qualify for the SEWAGE EXPERT gold star and will surely score well on the final exam.
ANSWER: Both designs are EQUALLY EFFICIENT at removing about 85 to 95% of the input EBOM and both destroy about 99.9% of the pathogens. Both FINAL EFFLUENTS have the same composition and are rich in mineral nutrients like phosphate, nitrate and sulfate. Their initial and operational costs are however different. Generally, TF plants are less expensive to build and to run if land is not EXPENSIVE as they do not require the pumping of large quantities of air into aeration tanks. Conversely, AS systems are more expensive to build and operate. However, the advantage of the AS system is that it can treat LARGER VOLUMES of sewage in a SMALLER SPACE than can TF systems. AS aeration tanks can be stacked up in buildings whereas TF systems can not. Since most land near cities (where the sewage is!) these days is darn near worth its weigh in gold, AS systems are replacing TF systems. A prime example of that is seen in Moscow where they are installing an AS system to replace the TF system.
Neither of the two secondary treatment plants do the following:
![]() They do NOT KILL ALL THE PATHOGENS,
particularly certain viruses and protozoan spores that survive passage
through the entire plant.
They do NOT KILL ALL THE PATHOGENS,
particularly certain viruses and protozoan spores that survive passage
through the entire plant.
![]() They do NOT DIGEST MANY MAN-MADE ORGANIC CHEMICALS
such as pesticides and herbicides.
They do NOT DIGEST MANY MAN-MADE ORGANIC CHEMICALS
such as pesticides and herbicides.
![]() They do NOT REMOVE TOXIC METALS like
cadmium, mercury, and lead. Rather these chemicals, which usually come
from industrial process, end up in the sludge.
They do NOT REMOVE TOXIC METALS like
cadmium, mercury, and lead. Rather these chemicals, which usually come
from industrial process, end up in the sludge.
![]() It does NOT PRODUCE POTABLE WATER.
Any water that comes out of the pipe of a secondary sewage treatment plant
must be further treated before it is safe to drink.
It does NOT PRODUCE POTABLE WATER.
Any water that comes out of the pipe of a secondary sewage treatment plant
must be further treated before it is safe to drink.
Another component of the problem harks back to the matter of perspective discussed previously. People resent paying high fees for something that seems in abundant supply. Further, they resent limitations on their use of water for lawns and washing their cars.
![]() How many of you would not take a job in a community that wouldn't let you
wash your car or have a lawn?
How many of you would not take a job in a community that wouldn't let you
wash your car or have a lawn?
When your water source is polluted it obviously must be purified before you will use it in your homes. However, the purification process costs significant money (e.g. user fees and/or taxes). Also the supply systems required for bringing water to homes and for removing the waste water are expensive and need occasional repairs. Since most of us obtain our water from surface sources (e.g. rivers and lakes) how do we control the pollution of these sources? For example, suppose your community's water comes from a river that runs by a city in another state that city DUMPS RAW SEWAGE into the river thereby SAVING ITS CITIZENS the money it would take to build a STP. This means your community has to pay to remove the pollution added by the people upstream. What do you do about that? Go to war with the other city? Pay the extra price and shut up? Sue the SOBs? Move to the city upstream? Fortunately, this is currently not a problem because of the Federal & state regulations that require communities to clean up their waste waters. However, some people are suggesting that this might change if this control is returned to the States. What do you think? Will Idaho citizens tax themselves to clean up their wastes so Washington citizen won't have to spend money removing the Idaho pollutants? Recently a local politician was quoted as being "unable to see how cattle grazing in the wild could be a pollution problem"; obviously the cattle this person was familiar with were toilet-trained & didn't poop near any streams.
![]() CHEMICAL
FLOCCULATION. In this process (also called coagulation) certain
nontoxic metal salts like IRON or ALUMINUM
are mixed with the water. Then a chemical is added that forms a HEAVY
PRECIPITATE (called a floc) that traps particles, including
viruses, bacteria, clay etc. and settles to the bottom as sludge.
CHEMICAL
FLOCCULATION. In this process (also called coagulation) certain
nontoxic metal salts like IRON or ALUMINUM
are mixed with the water. Then a chemical is added that forms a HEAVY
PRECIPITATE (called a floc) that traps particles, including
viruses, bacteria, clay etc. and settles to the bottom as sludge.
![]() The cleared effluent is then FILTERED
through beds of GRADED SAND AND ROCK
to remove the majority of the remaining particles.
The cleared effluent is then FILTERED
through beds of GRADED SAND AND ROCK
to remove the majority of the remaining particles.
![]() The filtered effluent is treated with chlorine to kill any remaining pathogens.
It does not render the water sterile however and some pathogens are resistant
to the normal levels of chlorine used.
The filtered effluent is treated with chlorine to kill any remaining pathogens.
It does not render the water sterile however and some pathogens are resistant
to the normal levels of chlorine used.
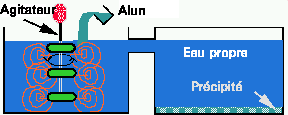
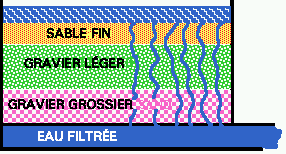
Figure 15. The basics of water purification. Polluted water, generally from a reservoir where it has been stored for several months, is pumped into a large mixing tank and Al or Fe salts are mixed in forming a voluminous precipitate. This precipitate traps most of the larger suspended matter of bacteria, algae, viruses and dirt. The mixture is pumped to a settling tank (Fig. 4). The supernatant is then filtered through layers of graded sand beds. This filtration removes most of the remaining pollutants. Finally the water is chlorinated before being sent out to the users.
These water purification facilities can be placed in large building; the sand beds being stacked one on top of the other. However, this treatment does not remove such pollutants as radioactive elements, many organic chemicals and some heavy metals. A common problem around the US today is that the high pollution of many water supplies OVERPOWER the ability of the current purification plants to entirely remove pollutants. Thus in many cities of the US the citizens are told NOT TO DRINK THE TAP WATER, but to drink bottled water. This obviously present a dilemma; while paying taxes to build improved water purification facilities may seem undesirable to many, having to buy bottled water amounts to a "TAX". Alternatively, larger doses of chlorine may be added to correct the deficiencies of the purification plant. When the quality of tap water is suspected or when it contains high amounts of chlorine, many people install home purifying systems. Again, this amounts to a hidden TAX for pure water. In addition, a problem with these home-water-purification units is that home owners are unable to VERIFY that the units are DOING THEIR JOB, whereas the municipal facilities have to follow rigorous purity regulations (State & Federal) that require frequent testing of the water for pollutants by trained laboratory personnel. Some people are concerned that if Federal water quality regulations are relaxed the US water quality will further deteriorate. Does this possibility concern you?
Because bottled water is INCONVENIENT
and EXPENSIVE many people install "HOME
PURIFICATION SYSTEMS" to remove pollutants. I'm unable to go
into a detailed description of the design of these products as there are
too many of them and more are appearing all the time as the problem grows.
However, the bulk of these units involve ONE OR
BOTH of the following components: a FILTRATION
SYSTEM to remove microbes and other particles from the tap water
and/or ION EXCHANGE
RESINS or ACTIVATED CHARCOAL
to remove the soluble dangerous minerals (lead, cadmium, mercury.) and/or
organics (pesticides, industrial pollutants). The ion exchange resins are
the same things used in water softening tanks. Activated charcoal is a
form of carbon that has the characteristic of ABSORBING
large quantities of organic matter. The filters filter out particles based
on the size of the holes in the filters.
![]() FAQ about the
Home Purification Units are "Are these units
effective? and Are they worth
buying?":
FAQ about the
Home Purification Units are "Are these units
effective? and Are they worth
buying?":
ARE THEY EFFECTIVE?
![]() Some of them are VERY EFFECTIVE when
USED
AS DESIGNED. That is, you have to KNOW
EXACTLY what you are doing before you decide to purchase one
of these units. If for example, you are concerned about DANGEROUS
METALS like lead, you must purchase
a unit (a) that is designed to remove METAL
pollutants and not something else (like viruses) and (b) that will remove
these pollutants at the RATE you use
the water.
Some of them are VERY EFFECTIVE when
USED
AS DESIGNED. That is, you have to KNOW
EXACTLY what you are doing before you decide to purchase one
of these units. If for example, you are concerned about DANGEROUS
METALS like lead, you must purchase
a unit (a) that is designed to remove METAL
pollutants and not something else (like viruses) and (b) that will remove
these pollutants at the RATE you use
the water.
![]() All these units FAIL eventually. The
more pollutants in the water the sooner they FAIL;
the more water you put through them the sooner they FAIL.
This means you must REPLACE THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS,
usually some form of expensive cartridge, at intervals. When they fail
they can CAUSE a pollution problem.
A major question you should ask before purchase is "How
do you know when a unit is no longer working?"
All these units FAIL eventually. The
more pollutants in the water the sooner they FAIL;
the more water you put through them the sooner they FAIL.
This means you must REPLACE THE CRITICAL COMPONENTS,
usually some form of expensive cartridge, at intervals. When they fail
they can CAUSE a pollution problem.
A major question you should ask before purchase is "How
do you know when a unit is no longer working?"
![]() The buyer must take the RESPONSIBILITY
of deciding the kind of unit needed, where it will be placed etc.. The
companies selling these items often do not completely inform the buyer
as to their design or the sales persons may not be an expert on this item
or understand your needs. As is often the case, advertising may OVER-PROMISE
the efficacy of a unit or its long term expense.
The buyer must take the RESPONSIBILITY
of deciding the kind of unit needed, where it will be placed etc.. The
companies selling these items often do not completely inform the buyer
as to their design or the sales persons may not be an expert on this item
or understand your needs. As is often the case, advertising may OVER-PROMISE
the efficacy of a unit or its long term expense.
![]() They are only effective if properly used. Small children enjoy drinking
from the ends of hoses or the faucets of bathtubs etc., so a unit on the
kitchen sink is probably only going to protect your children a limited
percentage of the time. Also do the neighbors, schools and Malls have similar
units purifying the water your children and you drink outside the home?
They are only effective if properly used. Small children enjoy drinking
from the ends of hoses or the faucets of bathtubs etc., so a unit on the
kitchen sink is probably only going to protect your children a limited
percentage of the time. Also do the neighbors, schools and Malls have similar
units purifying the water your children and you drink outside the home?
ARE THEY WORTH BUYING?
![]() Certainly, if the water is dangerously polluted and there is NO
OTHER REASONABLE ALTERNATIVE. Remember, however that the more
expensive the unit the better it probably is.
Certainly, if the water is dangerously polluted and there is NO
OTHER REASONABLE ALTERNATIVE. Remember, however that the more
expensive the unit the better it probably is.
![]() Before purchasing determine the LONG TERM COST,
including replacement costs of disposable components. Companies often make
a LARGER PROFIT on replacement parts,
because you are committed to using what you have already purchased.
Before purchasing determine the LONG TERM COST,
including replacement costs of disposable components. Companies often make
a LARGER PROFIT on replacement parts,
because you are committed to using what you have already purchased.
![]() I recommend that before purchasing one contact the local governmental agency
in charge of supplying the community's potable water and find out EXACTLY
WHAT THE PROBLEMS are. They'll have data defining the pollutants
and their quantities in your tap water. They usually can't recommend a
particular brand, but armed with that information you are in a much better
position to make the correct choice as to which unit to purchase.
I recommend that before purchasing one contact the local governmental agency
in charge of supplying the community's potable water and find out EXACTLY
WHAT THE PROBLEMS are. They'll have data defining the pollutants
and their quantities in your tap water. They usually can't recommend a
particular brand, but armed with that information you are in a much better
position to make the correct choice as to which unit to purchase.
![]() Finally, my PERSONAL PERSPECTIVE is
that I do not mind paying taxes for a SAFE AND
PLENTIFUL WATER SUPPLY.
I am willing to pay a LOT for a GUARANTEE
that no matter WHERE I GO in my community
(or my country for that matter) the water my family drinks will be safe.
Few people have the expertise to assess the chemicals and microbial quality
of drinking water, but properly run government agencies, employing trained
personnel and quality analytical equipment, have a much better chance of
producing pure water than you or I do.
Finally, my PERSONAL PERSPECTIVE is
that I do not mind paying taxes for a SAFE AND
PLENTIFUL WATER SUPPLY.
I am willing to pay a LOT for a GUARANTEE
that no matter WHERE I GO in my community
(or my country for that matter) the water my family drinks will be safe.
Few people have the expertise to assess the chemicals and microbial quality
of drinking water, but properly run government agencies, employing trained
personnel and quality analytical equipment, have a much better chance of
producing pure water than you or I do.
One of the COSTS that
is important to me is the ![]() PEACE OF MIND
PEACE OF MIND![]() that the water I drink is free of all the nasty things described below
(and a lot we're not going to get to). Added to this is the fact that once
you have one of these units you have added another responsibility to your
already FULL AND BUSY LIFE: you must
remember to maintain, replace, clean etc. that new Monkey-On-Your-Back.
that the water I drink is free of all the nasty things described below
(and a lot we're not going to get to). Added to this is the fact that once
you have one of these units you have added another responsibility to your
already FULL AND BUSY LIFE: you must
remember to maintain, replace, clean etc. that new Monkey-On-Your-Back.
Now I am going to tell you something that you definitely will not like to hear: IF YOU GET SICK FROM POLLUTED WATER IT WILL MEAN THAT YOU HAVE DRUNK WATER CONTAINING HUMAN OR OTHER ANIMAL EXCREMENT. I obviously can't speak for anyone else, but I would be willing to pay a lot of money to insure that that doesn't happen to me; how about you?
The US FDA has published a Hand Book on water and food borne diseases that is more complete than the material given below. Starting in the Spring of 1997 you will be held on exams for the information in that Hand Book on the diseases covered below, with the FOLLOWING EXCEPTIONS: You don't have to know the diagnostic procedures employed to detect and identify the organism; you don't have to know the recent research etc. that requires you to follow other LINKS on the net (but they might be interesting to examine?).
![]() To learn how these diseases are transmitted.
To learn how these diseases are transmitted.
![]() To learn how we can prevent their transmission.
To learn how we can prevent their transmission.
You might wonder why should we concern ourselves with a disease most of you probably have never heard of and certainly don't relate to being a problem in the US. Historically, cholera was an important disease in the US until sanitation measures took hold at the beginning of this century. Many more Settlers migrating West died from cholera and typhoid than ever died from Indian attacks. Water on the wagon trains was obtained from barrels using a common drinking cup. What likely happened was that when a member of the wagon train felt the call of nature they would go off into the grass, answer the call and them, like as not, get a drink. Since REST STOPS were rare, water scarce and ignorance rampant, few people washed their hands after relieving themselves of their bodily wastes. So when they dipped the drinking cup and part of their hand in the COMMON water barrel, anything clinging to their hands would be added to the water. Hence water borne disease spread quickly through many a wagon train.
In 1991 a cholera epidemic appeared in Peru and it has been spreading throughout South America ever since. By 1992 there had been 102 cases recorded in the US, mostly from people traveling in SA. There is a constant flow of immigrants, legal and illegal, entering the US from Central and South Am. and they bring with them all the diseases that are endemic to the areas they leave. It is likely that we have a sufficient pool of CHOLERA CARRIERS in the US to start an epidemic if the water supply should ever fail (earthquake, volcanic eruption etc.). We would be wise to remain vigilant where this disease is concerned.
The bad news is that there is currently NO EFFECTIVE VACCINE for cholera and once the disease hits it is too late for antibiotics to do any good. The good news is that the treatment is CHEAP AND READILY AVAILABLE if applied at the first symptoms.
![]() 1/2 teaspoon salt
1/2 teaspoon salt
![]() 1/4 teaspoon potassium or sodium bicarbonate or citrate
1/4 teaspoon potassium or sodium bicarbonate or citrate
![]() 1/4 teaspoon of potassium chloride
1/4 teaspoon of potassium chloride
![]() 4 tablespoons of glucose, rice, wheat or potato flower
4 tablespoons of glucose, rice, wheat or potato flower
![]() Nurses,
for more on ORT see Sci. Am. May 1991 pg 50.
Nurses,
for more on ORT see Sci. Am. May 1991 pg 50.
A reasonable alternative formulation is Ricelyte or a sports-drink sold as a replacement drink for salts lost on hot days. The world wide application of ORT has greatly decreased the death from cholera. For example, cholera victims had a 50 to 60% chance of dying before ORT, but now 97% survive when given this treatment. In places where ORT has been vigorously applied the fatalities from diarrhea fell by as much as 50% and the cost of treatment for diarrhea declined by 75%. A word of warning here. BABIES die very quickly from dehydration and shock and there is a myth in many societies that if a baby is vomiting it should not be given liquids because it hurts them to vomit. THIS IS A SURE WAY TO KILL THE BABY. With few exceptions, a baby losing liquids by vomiting and diarrhea should be given ORT no matter how messy and dirty and VOMIT-COVERED you get (unless you consider a vomit-free house is more important than a live baby). However, ORT requires that busy mothers continuously monitor the sick child.
The prevention of cholera lies in SANITATION (personal & public) and a CLEAN WATER SUPPLY. If you keep fecal material out of the drinking water and off your food you ARE UNLIKELY TO GET CHOLERA. Travelers to countries with ENDEMIC cholera should not eat any food that has not been COOKED or drink anything but BOTTLED DRINKS or water you have BOILED or chemically purified yourself. Asymptomatic carriers exist and the natural reservoir of Cholera has recently been found to be MARINE LIFE. The cholera bacillus is generally not long lived out of its host except in polluted water.
Various strains differ in virulence. Generally, they invade cells lining the colon and lower small intestine and penetrate the underlying tissues. Their mechanisms of virulence are not totally understood, but exotoxins and endotoxin play a role. Recently a virulent strain of Salmonella enteritidis has appeared in chickens. This strain is particularly DANGEROUS because it infects the ovaries of the chicken and is introduced INSIDE the egg. With other chicken salmonella strains, the bacteria are ONLY IN THE FECES and a contaminated egg shell can be disinfected with a hot soapy wash or chlorine solution. However, the only way the internalized salmonella can be destroyed is by thoroughly HEATING THE EGG THROUGHOUT; that is, a "soft-boiled" or "sunny-side-up" egg is a gamble with your gut, if not your life (before doing this make sure you have a large supply of TP and are near to a toilet). Between 1985 and 1991 49 people died from this organism and >12,000 cases were recorded.
Most cases of Salmonellosis are self limiting, but babies and the elderly can die from the disease. Antibiotics do little good as many of the strains are resistant to numerous antibiotics due to the plasmids they carry. A carrier state is common. Because of the general good quality of the water supply, Salmonellosis is usually a food borne disease in the US. Therefore, to avoid this disease possibly contaminated food like poultry and beef should be sufficiently heated to kill any Salmonella anywhere within the meat. Products made from uncooked egg (e.g. hollandaise sauce) should be avoided unless heated.
There are three other strains of E. coli that produce diarrhea, but we will only be concerned with one of them, 0157:H7 which will be described in the section on food borne diseases.
Click here for a detailed discussion on Traveler's
diarrhea:

Figure 16. Electron micrograph of E. coli. Note the dividing cells and the "hairy nature of the cells. This latter is probably the LPS and maybe some capsular material or pili.
It is now recognized that 95% of the peptic ulcers and 100% of chronic gastritis is caused by H. pylori. It is also thought that this organism is the major cause of stomach cancer because it produces a persistent immune response that damages the stomach lining. It turns out that it grows in the mucus lining that protects the stomach cells from the strong acid. H. pylori is highly motile and propels itself through the thick mucus by its vigorous corkscrew-motility. Further, they are protected from the stomach's acid by the production of the enzyme urease that breaks down urea into ammonia which NEUTRALIZES the stomach acid in the local of H. pylori.
Its transmission may be via water & person to person, but this has not been rigorously proven yet. However, at least 20% of the people in the US are infected and perhaps many more. It is world wide and is found in a number of animals. Treatment is with antibiotics and bismuth compounds and several groups are working on a vaccine. There is still much to be learned about this organism and how it produces disease, however if it is a major cause of stomach cancer we may see a significant decline in this terrible disease (Sci. Am. Feb. 1996).
The problem is water contaminated with human wastes and food handlers that spread the virus while preparing food during the INCUBATION PERIOD before they become ill. Being a virus, there is no treatment except for the GG. A typical SCENARIO is an announcement in the paper and over the TV that "Everyone who ate at ________ during the period from ___ to ___ should go to their doctor and receive a GG shot". It is a common disease and anywhere from 20 to 80% of a given population will have Ab against this virus. Apparently many people have a mild version in childhood. It is occasionally lethal.
The reservoirs include beavers, dogs, cats, raccoons and humans. Prevention includes boiling the water or treating it with chlorine or iodine; but it may take several hours in cold water to kill the cyst. It can be treated with anti-protozoan drugs. In NW most people seem to contract it from drinking from "pure mountain streams". With the increased human population, it is unwise to consider that any drinking water in the "wild" is safe any longer. Humans generally do not bury their fecal wastes in the woods deep enough to prevent them being washed into nearby streams and lakes. In addition the animals reservoirs continually contaminate the streams and lakes.
The disease, AMOEBIC DYSENTERY, is characterized by diarrhea, abdominal pain and blood in the feces, however it is rarely fatal. Rather, it is CHRONIC INFECTION that ultimately shortens lives. It is primarily transmitted by fecally polluted water. The organism can invade other tissues including the liver resulting in severe liver damage and early death. It can be treated by anti-protozoan drugs, but once it leaves the intestine it is often impossible to cure.
ANSWER: The cheap answer is because so many humans remain ignorant of basic sanitation procedures and/or are too stubborn to apply them. Certainly, ignorance is a major cause of WBDs. However, even people who know the proper sanitation measures are often unable to apply them because of a lack of personal or community resources. Good sanitation is equally a personal and community thing. It is of little help if you are personally clean, but you are immersed in a world of contaminated food and water. No matter how vigilant you are it is likely that you will contact a WBD. Often governments feel it is better to spend their limited resources on arms or industrial development rather than on a clean water or food supply. Where the mass of the population is poor, the wealthy often refuse to help pay for sanitation. As you will see in one of the tapes (Cell Wars) shown in lab, sanitary measures are difficult to apply.
Did you hear about the doctor who divorced his wife when he learned that she was eating an apple-a-day?
Le principe de base de la bioréhabilitation est le même que pour le traitement des effluents: utiliser le métabolisme des micro-organismes pour métaboliser des polluants et les convertir en composés innofensifs. La bioréhabilitation passe généralement par les étapes suivantes:
![]() Définir
le problème de pollution: quelles sont les substances présentes;
en quelles quantités; quelle est leur toxicité; s'accumulent-elles
et si oui, à quel rythme?
Définir
le problème de pollution: quelles sont les substances présentes;
en quelles quantités; quelle est leur toxicité; s'accumulent-elles
et si oui, à quel rythme?
![]() Développer
une approche de traitement basée sur les micro-organismes.
Développer
une approche de traitement basée sur les micro-organismes.
![]() Isoler
un(des) micro-organismes qui métabolisera(ont) le(s) polluants(s).
Isoler
un(des) micro-organismes qui métabolisera(ont) le(s) polluants(s).
![]() Faire
croître une population importante de ces micro-organismes.
Faire
croître une population importante de ces micro-organismes.
![]() Introduire
ces micro-organismes dans l'environnement pollué en leur donnant
les éléments nutritifs et les conditions de croissance optimales.
Introduire
ces micro-organismes dans l'environnement pollué en leur donnant
les éléments nutritifs et les conditions de croissance optimales.
L'élément essentiel consiste à trouver les BONS MICROBES. Un moyen d'y arriver consiste à employer une TECHNIQUE D'ENRICHISSEMENT DE CULTURE:
SCIENCE HALL, ROOM 440CA
PHONE: 509-335-5108
FAX: 509-335-1907
E-mail address:
hurlbert@wsu.edu hurlbert@pullman.com
OFFICE HOURS: M,W 1:30 to 3:30 PM.