![]() What the BASIC
TOOLS of GE how are and how they work.
What the BASIC
TOOLS of GE how are and how they work.
![]() How GENE
CLONING is carried out.
How GENE
CLONING is carried out.
![]() How DNA can be
used to IDENTIFY all living organisms
How DNA can be
used to IDENTIFY all living organisms
![]() How we can DETECT
very TINY QUANTITIES of DNA even when
they may be millions of years old.
How we can DETECT
very TINY QUANTITIES of DNA even when
they may be millions of years old.
![]() In addition, ETHICAL
problems of the GE revolution will be presented and some possible ways
of dealing with them considered.
In addition, ETHICAL
problems of the GE revolution will be presented and some possible ways
of dealing with them considered.
I have listed some of the changes you may experience within your lifetime, indeed some within the next few years. With the sequencing of the ENTIRE HUMAN GENOME anticipated around the turn of the century, a whole new set of possibilities will be unlocked. Currently (Fall 1996) we have sequenced >10,000 of the ~100,000 human genes, and the rate of sequencing is accelerating as sequencing techniques are improved. About 3,000 human genetic diseases are currently known. This means that approximately 14% of newborns are afflicted with a "visible" genetic disease. This does not begin to include the genetic-based "tendencies" (to develop cancer, arthritis, TB, colds, asthma, flu etc.) and/or "conditions" which all of us have; what genetic conditions do you have? For example, I and my half brother suffer from a genetic condition called Celiac Sprue, which means that wheat protein (gluten) does bad things to the cells in our intestine and we can't eat pizza etc. However, we are FINE as long as we don't eat wheat products. Sprue is a common genetic "condition" that effects up to 25% of the Irish and lessor numbers of other ethnic groups. How many reading this are Irish? Some of you suffer allergies, nearsightedness, migraines, etc., all of which have their basis in your genome. Once the human genome is mapped we can not only identify the particular alleles each of us have, but we will eventually figure a way to replace "undesirable genes" with "good genes".
![]() CRITICAL THINKING
QUESTION: How do we as individuals and a society define "good
and bad" genes? For example, if it turns out that genes are
at the basis of alcoholism or homosexuality
or child molestation or manic
depression, do we set out to "cure" people of these genes? If a
"homosexual" gene is found, what would you
do if you found a fetus of yours was carrying that gene?
CRITICAL THINKING
QUESTION: How do we as individuals and a society define "good
and bad" genes? For example, if it turns out that genes are
at the basis of alcoholism or homosexuality
or child molestation or manic
depression, do we set out to "cure" people of these genes? If a
"homosexual" gene is found, what would you
do if you found a fetus of yours was carrying that gene?
One current problem with the genetic revolution is that knowing which gene causes a disease condition and being able to identify the presence of that gene in a person, doesn't mean we UNDERSTAND the molecular biology of the disease process, thus we usually CAN'T PREVENT or CURE the disease caused by a defective gene. An example of this TERRIBLE DILEMMA is that a number of genes that predispose women to breast cancer have been discovered (and new ones are continually being found). This raises important ethical and personal considerations.
![]() If a CURE or
PREVENTION is not possible, should a woman be told she carries such a gene?
If a CURE or
PREVENTION is not possible, should a woman be told she carries such a gene?
![]() If a cure or
prevention is NOT POSSIBLE, would you want to know you had a time-bomb
ticking in you?
If a cure or
prevention is NOT POSSIBLE, would you want to know you had a time-bomb
ticking in you?
![]() If a cure or
prevention is not possible, would you consider having your BREASTS REMOVED
to prevent getting the disease? If you decide to do this (and many women
have), without any sign of cancer, should the Health Insurance Co. pay
for the removal of a healthy breast because it is "elective" surgery?
If a cure or
prevention is not possible, would you consider having your BREASTS REMOVED
to prevent getting the disease? If you decide to do this (and many women
have), without any sign of cancer, should the Health Insurance Co. pay
for the removal of a healthy breast because it is "elective" surgery?
![]() Should one's mate,
boss, insurance Co., potential employer etc. have access to your genetic
information? Can you think of situations where it would be logical and
reasonable for others to have this information? How about the army? The
CIA?
Should one's mate,
boss, insurance Co., potential employer etc. have access to your genetic
information? Can you think of situations where it would be logical and
reasonable for others to have this information? How about the army? The
CIA?
![]() If you owned a life
insurance Co. would you give your political donations to a congressperson
who favored requiring potential policy holders to give this information
to their insurance Co.
If you owned a life
insurance Co. would you give your political donations to a congressperson
who favored requiring potential policy holders to give this information
to their insurance Co.
![]() Who pays for the
screening for disease-genes, the cost of which currently is high? Should
I have to pay for your screening & vice versa?
Who pays for the
screening for disease-genes, the cost of which currently is high? Should
I have to pay for your screening & vice versa?
![]() What if you control
the genetic information and you know that giving it out will lead to an
abortion; what would you do?
What if you control
the genetic information and you know that giving it out will lead to an
abortion; what would you do?
![]() What if you have
access to the genetic information of someone your daughter/son, sister/brother
etc. is going to marry and you don't think they've told them of a serious
genetic "condition". Would you tell?
Who owns your loyalty? What is ethical here?
What if you have
access to the genetic information of someone your daughter/son, sister/brother
etc. is going to marry and you don't think they've told them of a serious
genetic "condition". Would you tell?
Who owns your loyalty? What is ethical here?
A final reminder of anyone who is considering avoiding these problems; gene therapy trials are currently underway (but they're having problems working: TIME 10/9/95; Science 269:1050 [1995]), people are deciding to abort on the basic of the results of fetal genetic testing and the number of identified defective genes increases almost daily (and some of the ones they find will be ones you and I carry).
In the 1950s it had been noted that if one grew a particular bacteriophage on a particular bacterial mutant host strain (A) and then infected a bacterial mutant-strain (B), of the same species, with the phage A, the yield of phage from strain B was VERY LOW. However, if you took the few phage B that were produced and infected strain B with them, the phage yield was now NORMAL. Subsequently, in the 1960s, it was found that the phage DNA that grew on strain B had been CHEMICALLY MODIFIED so that it could not be cleaved (destroyed) by a DNase in strain B. The DNase involved in this cleavage was found to be somewhat specific, in that it mainly cut the DNA at CERTAIN SEQUENCES; unless these sequences had been CHEMICALLY MODIFIED by enzymes in the cell (missing in strain A). All previous DNases cut DNA randomly, so this finding suggested that DNA could be cut up into SPECIFIC FRAGMENTS which would ALWAYS contain the SAME SET OF GENES between the cut-sites. However, these first "specific" DNases did not prove as SPECIFIC as hoped. Finally, in 1970 Hamilton Smith accidentally found that a DNase from the bacterium, Haemophilus influenzae, CUT DNA ONLY at UNIQUE DNA SEQUENCES known as PALINDROMIC SITES.
![]()
In DNA a PALINDROMIC SITE is a SEQUENCE OF BASE PAIRS in double stranded DNA that reads the same backwards and forward across the double strand. For example, the sequence of base pairs GAATTC is a palindrome because both sequences of the double strand READ THE SAME when read from either their respective "G" or "C" ends (COMPLEMENTARY strand = CTTAAG). The enzymes that cut these specific sites are calledRESTRICTION ENZYMES (RE). Based on the TYPES OF CUTS they make, there are two types of RE:
![]() One
group cuts straight across the double stranded DNA, producing BLUNT
ENDED DNA (Fig. 2).
One
group cuts straight across the double stranded DNA, producing BLUNT
ENDED DNA (Fig. 2).
![]() Another
type cuts the strand of DNA OFF THE CENTER
of the palindromic sites, but between the SAME
TWO BASES on the opposite strands. This leaves one or more bases
overhanging on each strand and such ends are called STICKY
ENDS (Fig. 1) because they form HYDROGEN
BONDS with their complementary cut counterparts.
Another
type cuts the strand of DNA OFF THE CENTER
of the palindromic sites, but between the SAME
TWO BASES on the opposite strands. This leaves one or more bases
overhanging on each strand and such ends are called STICKY
ENDS (Fig. 1) because they form HYDROGEN
BONDS with their complementary cut counterparts.
For example, in the base sequence GAATTC,
the RE that cuts this site cleaves the DNA between the "G"
and the "A" on each complementary
strand, thus leaving the overhangs of AATT & TTAA respectively
(Fig. 1). Over 200 different RE have been isolated that cut at many different
specific DNA sequences. They are all QUITE SPECIFIC
and
this specificity is the KEY to their use. REs that cut at 4, 5, 6, 8, 9,
and 11 base pair palindromic sites have been found. It follows that the
MORE BASE PAIRS in the palindromic site the LESS
LIKELY a site is to exist statistically. That is, a 4-base-cutting
RE cuts the same DNA many more times than an 8-base-cutter
does. The odd numbered cutting sites are not true DNA palindromes, in that
the central bp reads different in the two directions. For example AA?TT
is a 5 bp cutting site, where the ? = a number of different bases.
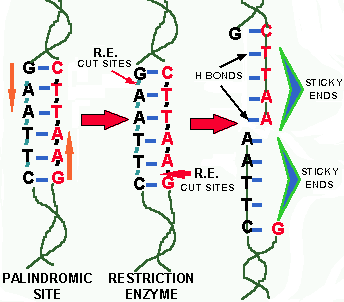
Figure 1. Sticky ended cut with restriction enzyme. The red arrows indicate the positions where the RE cuts the DNA. When the complementary stands pull away the "sticky end" overhangs are left.
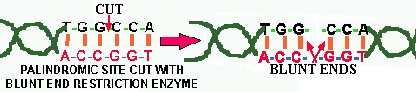
Figure 2. Blunt ended cuts by a restriction enzyme. Blunt end cutting REs cleave the DNA between two bases in the middle of a palindromic site.
![]() CRITICAL THINKING
QUESTION: The following are examples of RE DNA sites on a single strand.
Add the complementary bases and find the RE sites: CCTAGT; AATCCTAGGACG;
AAATTAATCGG; TAAGGCGCGCCTAAT; TACGCCAAGCTTGCATGCCTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGTATCCCCGGGTACCGAGCTCGAATTCACT.
CRITICAL THINKING
QUESTION: The following are examples of RE DNA sites on a single strand.
Add the complementary bases and find the RE sites: CCTAGT; AATCCTAGGACG;
AAATTAATCGG; TAAGGCGCGCCTAAT; TACGCCAAGCTTGCATGCCTGCAGGTCGACTCTAGAGTATCCCCGGGTACCGAGCTCGAATTCACT.
There are 10 RE sites in this last one, can you find all ten?
The final important component in genetic engineering is an enzyme called
LIGASE.
Ligase is an enzyme that covalently
joins
the sugar-phosphate backbone of bases together. Ligase is also involved
in DNA replication.
In effect LIGASE reverses the action of the RE, which breaks
the sugar-phosphate backbone-bonds. Ligase requires energy to form
these bonds (Fig. 3). Ligase will join either "sticky" ends or "blunt"
ends, but it is more efficient at closing sticky ends because the "sticky
overhangs" of these ends adds stability which holds the stands together
while the ligase works, whereas the blunt ends are LESS
STABLE. The sticky ends must have the SAME "base overhang" (Fig.
1), but ANY BLUNT END can be joined
to any other blunt end (Fig. 2).
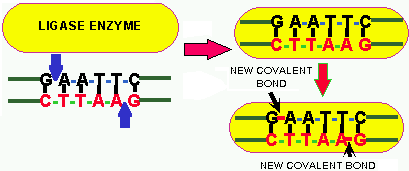
Figure 3. The ligase reaction. The sticky ends of two DNA strands line up according to their bp hydrogen bonding. The cut sites are indicated by the blue arrows. The ligase binds to the hydrogen-bonded DNA strands and forms covalent bonds between the two DNA ends (red bonds), thus joining them. Similarly, if the blunt ends of DNA come together the ligase can form covalent bonds between them.
Review of the components of GE:
![]() (1) Double-stranded
DNA contain palindromic restriction enzyme sites.
(1) Double-stranded
DNA contain palindromic restriction enzyme sites.
![]() (2) Many types of
restriction enzymes cut or cleave palindromic sites in the double-stranded
DNA sample forming either a sticky or a blunt end.
(2) Many types of
restriction enzymes cut or cleave palindromic sites in the double-stranded
DNA sample forming either a sticky or a blunt end.
![]() (3) The enzyme ligase
plus an energy source fuses or join two sticky or two blunt ends of DNA
together.
(3) The enzyme ligase
plus an energy source fuses or join two sticky or two blunt ends of DNA
together.
![]() Isolating the
SOURCE
and VECTOR DNA. The DNAs must be relatively
free of contaminating materials which interfere with the subsequent enzymatic
steps.
Isolating the
SOURCE
and VECTOR DNA. The DNAs must be relatively
free of contaminating materials which interfere with the subsequent enzymatic
steps.
![]() Both the source
and vector DNAs are cut with RESTRICTION ENZYMES.
When sticky ends are formed the DNA is cut with the same restriction enzyme(s),
but RE that produce blunts ends also work well in cloning.
Both the source
and vector DNAs are cut with RESTRICTION ENZYMES.
When sticky ends are formed the DNA is cut with the same restriction enzyme(s),
but RE that produce blunts ends also work well in cloning.
![]() The vector
and source DNAs are mixed with a LIGASE SYSTEM
and covalently bond together.
The vector
and source DNAs are mixed with a LIGASE SYSTEM
and covalently bond together.
![]() Finally, the
LIGATED
DNA is TRANSFORMED into
a host cell. Usually the host cell is a COMPETENT
bacterium,
but increasingly eukaryotic cells are being used. After suitable growth
has occurred the host cells are examined for the PRESENCE of the source
or CLONED DNA in its cytoplasm.
Finally, the
LIGATED
DNA is TRANSFORMED into
a host cell. Usually the host cell is a COMPETENT
bacterium,
but increasingly eukaryotic cells are being used. After suitable growth
has occurred the host cells are examined for the PRESENCE of the source
or CLONED DNA in its cytoplasm.
The entire cloning process often takes LESS THAN A DAY and is carried
out using volumes of 1,000 microliters or less. The examination of the
transformed host for the gene-of-interest may take an additional day or
so. A gene which has been successfully transferred in this way is said
to have been CLONED. The process is
referred to as "CLONING", "RECOMBINANT
DNA TECHNOLOGY", or "RECOMBINANT DNA".
These steps are summarized in the figure 4 below.
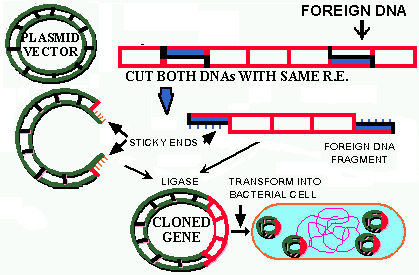
Figure 4. Cloning. For another figure illustrating cloning click here and view Fig. 11a.
![]() SEQUENCING:
Sequencing determines the base pair sequence of a gene. By reading the
3-letter code, sequencing also describes the AMINO
ACID SEQUENCE translated
from that gene.
SEQUENCING:
Sequencing determines the base pair sequence of a gene. By reading the
3-letter code, sequencing also describes the AMINO
ACID SEQUENCE translated
from that gene.
![]() MUTATION:
The gene bp sequence can be changed in specific ways and the modified gene
can be inserted back into its original host to see what each specific mutation
does. Whereas, spontaneous mutation is random, techniques are now available
that make it possible to CHANGE any
codon within a gene to any other codon. Therefore, it is possible to study
the effects of SINGLE AMINO ACID CHANGES
on the function of the gene product, which is, after all, the ultimate
purpose of the exercise.
MUTATION:
The gene bp sequence can be changed in specific ways and the modified gene
can be inserted back into its original host to see what each specific mutation
does. Whereas, spontaneous mutation is random, techniques are now available
that make it possible to CHANGE any
codon within a gene to any other codon. Therefore, it is possible to study
the effects of SINGLE AMINO ACID CHANGES
on the function of the gene product, which is, after all, the ultimate
purpose of the exercise.
![]() To replace
a mutated form of the gene in the original host cell with a healthy form
of the gene to see exactly what it does in its intended place of residence.
To replace
a mutated form of the gene in the original host cell with a healthy form
of the gene to see exactly what it does in its intended place of residence.
![]() To use the
amplified gene to make HUMONGOUS QUANTITIES
of the GENE PRODUCT for commercial
purposes. This is how products like human insulin, human growth hormone,
plasminogen activator, interlukins and the bovine milk hormone are all
produced.
To use the
amplified gene to make HUMONGOUS QUANTITIES
of the GENE PRODUCT for commercial
purposes. This is how products like human insulin, human growth hormone,
plasminogen activator, interlukins and the bovine milk hormone are all
produced.
![]() To INSERT the
gene into ANOTHER SPECIES for some purpose. Such animals or plants are
said to be TRANSGENIC.
For example, many crops are protected against caterpillar larvae because
a gene from a bacterium has been inserted into their cells. This gene produces
a protein that is HIGHLY, and SPECIFICALLY, TOXIC to the larvae of many
moths and butterflies that attack food crops.
To INSERT the
gene into ANOTHER SPECIES for some purpose. Such animals or plants are
said to be TRANSGENIC.
For example, many crops are protected against caterpillar larvae because
a gene from a bacterium has been inserted into their cells. This gene produces
a protein that is HIGHLY, and SPECIFICALLY, TOXIC to the larvae of many
moths and butterflies that attack food crops.
There is a DOWN SIDE of GE. The
same procedures that can be used to produce a better crop, or human insulin,
can also be employed to make a more POWERFUL PATHOGEN.
There is evidence that some countries have or are considering doing this.
For example, Iraq was apparently growing bacterial pathogens for biological
warfare, but it was deterred from using them when we threatened atomic
retaliation. It is only a small jump in "reasoning" to consider engineering
a "better pathogen" with which to destroy a hated enemy (fill
in blank--the news report that some Americans. consider anyone working
for the government to be the enemy). For more information read "The
spectra of biological weapons" Scientific Am. Dec. 1996,
pg. 60.
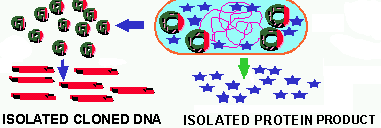
Figure 5. The use of gene cloning to amplify the cloned DNA and/or to produce lots of the cloned gene's product.
![]() CRITICAL THINKING
QUESTION: What should we do about regulating genetically engineered plants
and animals? Should we require that they be tested for safety, that they
be labeled as GE? Can you think of any other considerations regarding these
"products"? Will you eat "genetically engineered foods"?
CRITICAL THINKING
QUESTION: What should we do about regulating genetically engineered plants
and animals? Should we require that they be tested for safety, that they
be labeled as GE? Can you think of any other considerations regarding these
"products"? Will you eat "genetically engineered foods"?
The THREE basic principles required to understand DNA fingerprinting and all that follows from it you already know (the principle of ligand/receptor binding; see fig.2 chap 7), but it is worth taking a moment to review them.
![]() BASE-PAIRING
of AT (AU) & GC is the BASIC PRINCIPLE of this procedure. If you understand
this all else fall easily into place.
BASE-PAIRING
of AT (AU) & GC is the BASIC PRINCIPLE of this procedure. If you understand
this all else fall easily into place.
![]() SPECIFICITY
of
enzyme activity is the second CRUCIAL principle to understanding DNA fingerprinting.
This refers to the cutting of DNA by specific RESTRICTION ENZYMES at UNIQUE
palindromic sequences.
SPECIFICITY
of
enzyme activity is the second CRUCIAL principle to understanding DNA fingerprinting.
This refers to the cutting of DNA by specific RESTRICTION ENZYMES at UNIQUE
palindromic sequences.
![]() The recognition
that a CHANGE in a SINGLE BASE
PAIR (a mutation)
can either MAKE a RE-site where one did not exist previously or it can
REMOVE or ELIMINATE
a RE site from a gene. An analogy would be to "mutate" your phone number
by one letter; callers would get a different person.
The recognition
that a CHANGE in a SINGLE BASE
PAIR (a mutation)
can either MAKE a RE-site where one did not exist previously or it can
REMOVE or ELIMINATE
a RE site from a gene. An analogy would be to "mutate" your phone number
by one letter; callers would get a different person.
To understand DNA fingerprinting the double stranded DNA molecule must
be viewed as a chain with RANDOM RESTRICTION ENZYMES-sites
(palindromes) located along its length. If each of these various unique
restriction sites were marked with a different color, the DNA would appear
as a random multicolored stripped ribbon. If one set of unique restriction
enzyme sites were colored RED and the
appropriate RED-restriction enzyme
added, the DNA would be CLEAVED into a series of VARIOUS
SIZED FRAGMENTS depending on where the RED-SITES
were located along the DNA molecule (Fig. 6). It is easy to understand
that the group of DIFFERENT SIZED FRAGMENTS
would be UNIQUE for two DNA strands
with the RED-restriction sites located
at DIFFERENT PLACES along their respective
DNA double strands. The addition of a GREEN-restriction
enzyme that cut GREEN-SITES would produce
a different group of sized fragments. Each of these groups of restriction
enzyme-produced fragments would represent a unique FINGERPRINT
of that DNA (Fig. 6).
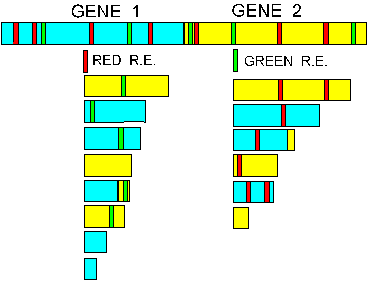
Figure 6. In this FIGURE there are two genes with the palindromic sites for two different restriction enzymes MARKED AS GREEN OR RED BARS. The number and size of the DNA fragments that would result if the DNA containing these two genes were cut with the respective restriction enzymes are shown. Determine the pattern you would get if you cut this DNA with BOTH ENZYMES at the SAME TIME; lay it out from the smallest to the largest fragment.
The DNA fragments are visualized using the technique known as GEL ELECTROPHORESIS, which you performed in lab exercise 15. Briefly, porous gels composed either of a PLASTIC called ACRYLAMIDE or of a derivative of agar, called AGAROSE, are used to separate DNA fragments based on size. The gels are prepared with wells into which the DNA fragments are ADDED. The gels are submerged, under an electrolyte buffer solution between a positive and a negative electrode; the DNA-containing solutions are added to the wells and the current is turned on. The DNA fragments are NEGATIVELY CHARGED so the wells containing them are placed closest to the negative electrode. When the current is turned on the DNA moves through the pores in the gel TOWARDS THE POSITIVE ELECTRODE. The shorter fragments move FASTEST because they are able to navigate through the pores of the gel more easily, whereas the longer DNA fragments move PROPORTIONALLY MORE SLOWLY through the pores. The result is a separation of the DNA fragments based on their length (SIZE). The DNAs are stained by dyes that binds to the DNA and fluoresces strongly when exposed to UV-light. The various sized DNA fragments appears as a series of bands that resemble a BAR CODE. See Fig. 13.
In Figure 7 the gel pattern of a hypothetical analysis of O.J.'s DNA
vs. a sample of unknown DNA is depicted. The two isolated DNAs were treated
with the same RE and the fragments separated on an agarose gel. Two unique
restriction enzyme fragment patterns are seen. The conclusion is that the
blood samples came from DIFFERENT INDIVIDUALS.
The SOURCE of the DNAs clearly influences the significance of these results.
For example, if the two samples were collected at the scene of the crime
it would mean one thing, but if the unknown DNA sample came from O.J.'s
shirt and it matched that of one of the victims at the scene of the crime,
the data takes on more significance.
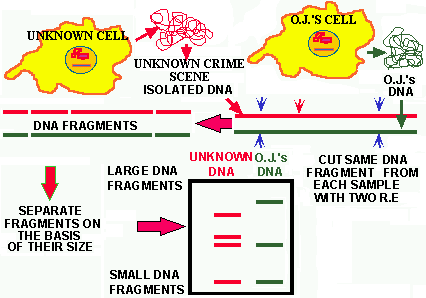
Figure 7. Clearly the DNA from the scene-of-the-crime is not that of O.J., as the fragment patterns (the DNA fingerprint) are different. Had they been the same what would that of said about the innocence or guilt of O.J.?
ANSWER: This is exactly what happens. When genomic DNA is treated with a RE and separated on a gel, what is seen is a continuous smear composed of 1,000s of individual DNA fragments. This problem is solved by a technique known as HYBRIDIZATION.
Hybridization again depends on the basic principle of HYDROGEN BONDING between GC & AT bonds in nucleic acids. The principles in the hybridization steps are:
![]() DNA strands
are SEPARATED by breaking the hydrogen
bonds between the bases with heat to produce SINGLE
STRANDS.
DNA strands
are SEPARATED by breaking the hydrogen
bonds between the bases with heat to produce SINGLE
STRANDS.
![]() Strand separation
is STRICTLY DEPENDENT
up on two factors: The TEMPERATURE
(amount of heat energy) and the NUMBER
of hydrogen bonds (an incorrect base pairing does NOT form H-bonds).
Strand separation
is STRICTLY DEPENDENT
up on two factors: The TEMPERATURE
(amount of heat energy) and the NUMBER
of hydrogen bonds (an incorrect base pairing does NOT form H-bonds).
![]() When the temperature
drops, single DNA strands in the same solution that are complementary SPONTANEOUSLY
COME TOGETHER by pairing up through their respective AT &
GC associations. The strength of their subsequent association depends on
the temperature and the total number of MATCHING base pairs.
When the temperature
drops, single DNA strands in the same solution that are complementary SPONTANEOUSLY
COME TOGETHER by pairing up through their respective AT &
GC associations. The strength of their subsequent association depends on
the temperature and the total number of MATCHING base pairs.
![]() The TEST
or SAMPLE DNA
is usually FIXED or BOUND
to a solid surface in a SINGLE-STRANDED STATE.
A piece of DNA of KNOWN SEQUENCE to
which something is attached that can be DETECTED
or SEEN is then mixed with the bound
DNA and the two are incubated together under conditions that will allow
COMPLEMENTARY
DNA sequences to join through the appropriate
hydrogen bonding. The DNA molecule which can be detected is called a PROBE.
The TEST
or SAMPLE DNA
is usually FIXED or BOUND
to a solid surface in a SINGLE-STRANDED STATE.
A piece of DNA of KNOWN SEQUENCE to
which something is attached that can be DETECTED
or SEEN is then mixed with the bound
DNA and the two are incubated together under conditions that will allow
COMPLEMENTARY
DNA sequences to join through the appropriate
hydrogen bonding. The DNA molecule which can be detected is called a PROBE.
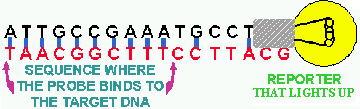
Figure 8. Hybridization probe. A short piece of DNA of known sequence (black bases) has a REPORTER substance attached to it. This reporter is usually a radioactive element like phosphorous-32 or an enzyme that induces light production from a substrate molecule and is indicated in this figure by the light bulb. If the probe sequence finds a complementary base sequence on the bound target or sample DNA, it will hydrogen-bond to it. When the excess, unbound probe is washed away the location of the bound probe and its complementary DNA can be detected by the REPORTER on the probe.
That is, the MORE hydrogen bonds there are the HIGHER
the temperature must be to completely SEPARATE
two DNA strands and to keep them separated. For example, if there were
two stands of DNA composed of 200 PERFECTLY complemented base pairs, then
it would take a temperature of 58oC. to separate them. However,
if only 199 of the base pairs were correct, it would only take 57oC.
to separate them; if there were only 100 correct base pairs the DNA strands
would fall apart at ~29oC; i.e., fewer bonds require less heat
(energy = lower temperatures) to rupture them.

Figure 9. In this figure a short piece of DNA, called the PROBE (Pink Star) is mixed with two different long DNA strands. One of these long strands contains a sequence of bp that exactly matches that of the probe, whereas the other differs with respect to a single bp (yellow oval). At 55oC the probe binds to BOTH long DNA molecules, however at 65oC the probe does not bind to the long DNA molecule with a single base pair mismatch. The probe is unable to bind to either long DNA molecule at 90oC. What do you think might be the results at a temperature of 60oC?
Hybridization is carried out as illustrated in Fig. 10:

Figure 10. The hybridization procedure.
The entire procedure is called HYBRIDIZATION.
Hybridization works because of the SEQUENCE OF
THE PROBE. A given probe will only bind with DNA
that is attached to the membrane IF IT FINDS a MATCHING
or COMPLEMENTARY DNA base pair sequence
that forms enough bonds to remain together under the heating
conditions used. Thus if no matching complementary sequences are found,
NO PROBE will bind (Fig. 10, green DNA). If
one or two of the 1,000s of the bound DNA fragments contain a sequence
complementary to the sequence in the probe, the probe will BIND only to
these fragments and thus become ATTACHED TO THE
MEMBRANE through this association with the complementary
membrane-bound-DNA
(Fig. 10, red DNA). It is possible
to chose probes that are known to bind to specific sequences or artificial
probes of KNOWN SEQUENCES can be made, for about $1.00/base and sent to
you in 48 hr.; THEY CAN BE ORDERED OVER THE INTERNET.

Figure 11. The original gel, shown in the middle, produces a smear of genomic DNA fragments (see Fig. 13). Within those 1000,s of fragments are the fragments shown on the left gel cut from a section of the two original DNA molecules shown in the upper left. When the smear of fragments, fixed to a membrane, are hybridized with the probe (DNA with attached reporter [green star], Fig. 8), the probe will HYBRIDIZE (bind) only to those fragments containing sequences of DNA that complement sequences present in the probe; i.e., those regions DIRECTLY BELOW the probe DNA. The location (pink ovals) of such complementary membrane-bound-fragments are shown on the gel at the right. Thus the detection system only "SEES" the pink ovals. See Fig. 13 for X-ray film detection of DNA fragments from a genomic DNA smear.

Figure 12. Homework project.
In Fig. 12 three different PROBES (A, B, & C) are hybridized against
the separated membrane-bound-DNA fragments shown on the right (from 3 duplicate
gels). As an exercise determine WHICH BANDS each of the three probes will
hybridize (bind) to; that is, draw three duplicate gels, 1, 2, & 3
and circle the band(s) in gel 1 that probe A will bind to; in gels 2 &
3 do the same with probes B & C respectively.

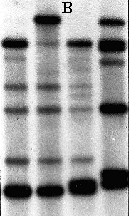

Figure 13. These are three experimental gels showing
the outcome of a hybridization procedure. Gel A shows the banding pattern
seen when genomic DNA, digested with a restriction enzyme, is separated
on an agarose gel. The smears in lanes 1 to 9 represent 1,000s of individual
DNA fragments produced by the restriction enzyme digestion. The banding
seen in these lanes is due to the high concentration of certain genes.
Gels B & C show examples of banding patterns obtained when genomic
DNA smears, bound to a membrane, are hybridized with specific
probes. The probes only bind, or hybridized to, a few of the
1,000s of fragments that contained base sequences COMPLEMENTARY to those
on the probe. Attached to the probes is substance which produces LIGHT
when treated with certain chemicals and this light is detected with photographic
film, in effect taking a picture of each of the locations where the probes
bind to a complementary DNA fragment on the membrane. ![]() click
here
and then click on "Hybridization" for some other cartoons of Southern
Blotting and illustrations of other molecular biology techniques.
click
here
and then click on "Hybridization" for some other cartoons of Southern
Blotting and illustrations of other molecular biology techniques.
Figure 14 illustrates how the blood from O.J.'s trial was tested to
determine matches. The DNA from the various samples of blood (from the
gloves, the Bronco, the socks, the bodies etc.) was extracted, digested
with one or more restriction enzymes, separated on gels, transferred to
DNA-binding membranes and hybridized with various probes. The pattern of
the DNA fragments (bands) from the samples that "lights up" were then compared
for similarities and differences.

Figure 14.
FAQ: About DNA fingerprinting.
1 How good (accurate) is it at identification. For example, is it as good as classical fingerprints?
Answer: In theory, with the exception of identical twins, EVERYONE on this planet has a different DNA fingerprint. That is, DNA fingerprinting IS as good (distinctive) as classical fingerprinting for identification.
2. What are its advantages?
Answer: In theory DNA fingerprinting will work with much smaller amounts of material than a classical fingerprint & DNA lasts much longer than classical fingerprints. DNA-containing samples that are many years old (up to 25 million yr.) are still usable. Only very tiny quantities of DNA are required in order to carry out a highly accurate test. For example, dried blood, semen, spit, skin etc. on samples stored in dusty files for years are still usable. Samples of mixed DNA's can also be used. DNA containing evidence is much harder to clean up at a crime scene than other evidence, like classical fingerprints.
3. What are its limitations?
Answer: There currently are no accepted Federal standards for controlling
the quality of DNA testing nationwide. Poor quality & poorly controlled
testing leads to QUESTIONABLE and SHODDY
RESULTS. Lab A may use one set of procedures and standards,
whereas, lab B may use another set of procedures and standards. Making
comparisons between results from the two labs difficult. The quality of
laboratory personal is not standardized. For example, clinical laboratory
technicians, that work in hospitals and clinical labs, must be certified
by their states and by a national organization that sets high standards
of training and experience. The clinical labs are frequently tested to
determine if their procedures are done correctly. They receive & must
analyze test samples whose composition is known by certification agencies.
The results are returned to the certification agencies for evaluation.
If a clinical lab makes too many errors the lab will be DECERTIFIED.
This is not yet the case with DNA testing facilities.
Do you think there should be a set of national standards for DNA testing or should each state set their own standards?
Even if there is a perfect match between DNAs, you can not say HOW the DNA containing sample got there or WHEN. In the O.J. trial a VALID question was raised about the possibility of evidence being planted. What makes this charge so powerful is the EXTREME SENSITIVITY of the procedure. That is, it would NOT BE DIFFICULT for someone to collect a small quantity of blood (one or two drops from a tube of a blood sample), body fluid or tissue from a victim (e.g. hair in a comb, blood on a Kleenex etc. ) and place this material where it would incriminate an innocent person. There are documented cases where quantities of drugs, marked money etc. have been "planted" and innocent people convicted of crimes because of these actions.
Finally, blood that is mixed with the wrong chemicals or is degraded is difficult to analyze accurately.
4. When faced with DNA evidence what questions should be asked?
Answer: As indicated above (and in the O.J. trial), questions regarding the handling of the evidence, the quality of the testing, including the quality controls used, the skill of the testing personnel, the accuracy of the data interpretation, possible contamination of the evidence, the possibility of accidental, or intentional misplacement of evidence are all valid questions that should be raised regarding DNA evidence (or any evidence for that matter). As the sensitivity of this powerful technique improves and its use widens throughout our justice system, it is important that we deal with these problems if we expect EQUAL JUSTICE for all. We must not lose sight of the fact that no matter how powerful a new tool in crime fighting is, its ultimate effectiveness is only as good as the persons using that tool.
![]() Do you think
O.J. did it and if so, how would you have voted based only on the evidence
had you been a jury member?
Do you think
O.J. did it and if so, how would you have voted based only on the evidence
had you been a jury member?
The PCR is another one of these discoveries, like that of the structure of DNA, the transforming factor determining the chemical nature of DNA, and restriction enzymes, that generated a quantum leap in science. Almost the instant after PCR is explained to a biological scientist, ideas as to its uses begin to pour from all but the most dull scientific mind. Even today, years after its discovery, we are still developing new uses for PCR.
The irony of the PCR is that living organisms have been doing it since they evolved in the primeval organic soup of this planet 3.5 billion years ago and scientists have been aware of the general DETAILS of this process for ~50 years. To put it succinctly, the PCR does in the test tube what every bacterium does in its tube of media or on an agar-plate and each of us do every day; we all produce billions of exact copies of our own DNA; AMPLIFYING our DNA millions of time. The enzyme DNA polymerase was discovered in the 1950s and our knowledge of the process has been increasing ever since. This means that thousands of scientists have studied DNA replication for 40 years without tumbling to PCR.
The basic principle of PCR is shown in Fig. 15. It has been know for a long time that DNA polymerase requires a short stand of DNA or RNA called a PRIMER to "prime" the START OF DNA REPLICATION. Mullis's genius was that he reasoned "That if you added the following components to a test tube containing a single DNA molecule, you could replicate & amplify that DNA molecule many million fold in a short time.
The components are:
![]() A sample of the
TARGET
DNA to be copied. In theory only a single molecule is needed.
A sample of the
TARGET
DNA to be copied. In theory only a single molecule is needed.
![]() A set of short (15
to 40 bases) single stranded PRIMERS
of DNA, in EXCESS, that will bind to
complementary regions of the opposing stands of the TARGET
DNA molecule . These primers
the region of DNA to be amplified.
A set of short (15
to 40 bases) single stranded PRIMERS
of DNA, in EXCESS, that will bind to
complementary regions of the opposing stands of the TARGET
DNA molecule . These primers
the region of DNA to be amplified.
![]() An EXCESS of the
4 nucleotide triphosphates, ATP, GTP, CTP, TTP.
An EXCESS of the
4 nucleotide triphosphates, ATP, GTP, CTP, TTP.
![]() The enzyme, DNA
polymerase.
The enzyme, DNA
polymerase.
![]() Various buffers
and cofactors like magnesium ions required by DNA polymerase.
Various buffers
and cofactors like magnesium ions required by DNA polymerase.
The final trick was to get the two target DNA stands APART
(separated) so the primers could bind and the DNA polymerase could do its
thing. It had been known for ~50 years that heat separates DNA stands and
that complementary strands then rejoin through base pairing when the temperature
is subsequently lowered. So Mullis heated his mixture of target DNA, primers
and triphosphate nucleotides to about 90oC for a few minutes
to separate the target DNA. He then lowered the temperature enough to allow
the primers, which were small and in VAST EXCESS,
to bind (ANNEAL) to their respective
complementary target DNA bp-sequences. At this point he added DNA polymerase
and allowed the polymerization reaction with the triphosphate nucleotides
to occur. That is, the DNA polymerase FILLED IN
the missing portion of each strand making TWO
NEW DOUBLE STRANDED regions of DNA.
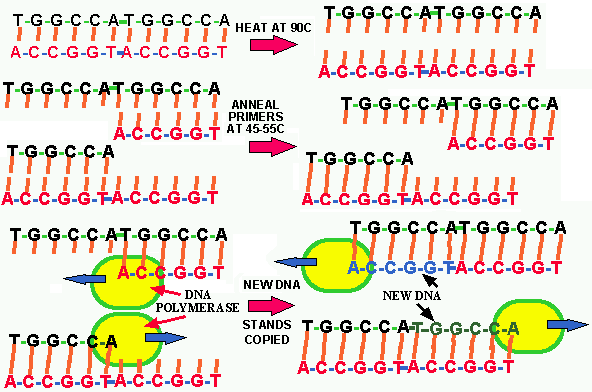

Figure 15. The polymerase chain reaction.
For another figure illustrating the PCR ![]() click
here and view the "PCR" link.
click
here and view the "PCR" link.
Each entire PCR cycle takes only 2 to 10 minutes. However, there was
one problem with the system devised by K. Mullis, which was that the DNA
polymerase he used was DESTROYED BY
THE HEATING process. Mullis had to add new DNA polymerase for
EACH ROUND, which was time-consuming and expensive. This problem was solved
by using HEAT-RESISTANT DNA polymerase
that only needed to be added once. THERMOPHILIC
bacteria that live in boiling hot springs have been described previously.
This is another case of SERENDIPITOUS BASIC SCIENCE turning out to be important.
The study of thermophiles might seem to be a waste of money and time to
many people as these bacteria, while certainly interesting, don't cause
disease in man or any other life form. The argument could be made that
a scientist could better spend his/her time working on cancer or some other
terrible disease that afflicts humankind. However, it turns out that since
thermophilic DNA polymerases tolerate high temperatures (e.g. 90oC)
for long periods without being destroyed, they are the perfect solution
to the PCR DNA polymerase problem. Thus today PCR has become a revolutionary
tool because of scientists who studied these odd thermophiles.

Figure 16. This figure represents another perspective of the PCR reaction. Of particular note is the use of the PCR to AMPLIFY SPECIFIC DNA SEGMENTS dependent on the PRIMERS EMPLOYED. By choosing primers with unique sequences one BRACKETS a known length (gene[s])of a DNA molecule. The bracketed segment is indicated by the dashed lines. The red and blue primers, by their COMPLEMENTARY BINDING to bp-sequences on the two respective parental DNA strands insure that ONLY the portion of DNA between them will be amplified. Five cycles of replication are shown, except that the last cycle is incomplete. Note that the number of DNA molecules increases EXPONENTIALLY with each cycle of replication.
The standard PCR reaction is run through about 30 cycles in a couple of hours which results in the amplification of the original DNA by over a 109 fold. Thus a single specific DNA region can be amplified to yield sufficient quantities to do anything that can be done with bulk-isolated DNA. In the case of crime evidence this means that the DNA in a single hair follicle, a single drop of semen or blood is sufficient to prove that an individual was present at the scene of a crime. Indeed any piece of evidence that contains one or more moderately long DNA fragments (e.g. >200 base pairs) can be amplified with PCR and its RFLP determined for identification purposes---or maybe to build a dinosaur eventually. However, at present the maximum limit for amplification is approximately 42 kilobases.
![]() The major limitations
of DNA fingerprinting are human error and the quality of the technology
used.
The major limitations
of DNA fingerprinting are human error and the quality of the technology
used.
![]() The discovery
of PCR increased the sensitivity and versatility of DNA fingerprinting,
and changed the face of molecular biology.
The discovery
of PCR increased the sensitivity and versatility of DNA fingerprinting,
and changed the face of molecular biology.
![]() These techniques
will allow infectious diseases to be identified within hours or even minutes.
They are accelerating the rate of sequencing the human genome, they allow
the investigation of complex ecological interactions and species relationships
that here-to-fore have been too complex to study.
These techniques
will allow infectious diseases to be identified within hours or even minutes.
They are accelerating the rate of sequencing the human genome, they allow
the investigation of complex ecological interactions and species relationships
that here-to-fore have been too complex to study.
WELCOME TO THE NEW WORLD OF GENETIC ENGINEERING; JUST KEEP YOUR SEAT BELTS FASTENED BECAUSE IT IS GOING TO BE A WILD RIDE.